Thermostat: | The thermostat acts a control, monitoring the temperature of the house, and brings the furnace on when the house needs to be heated. |
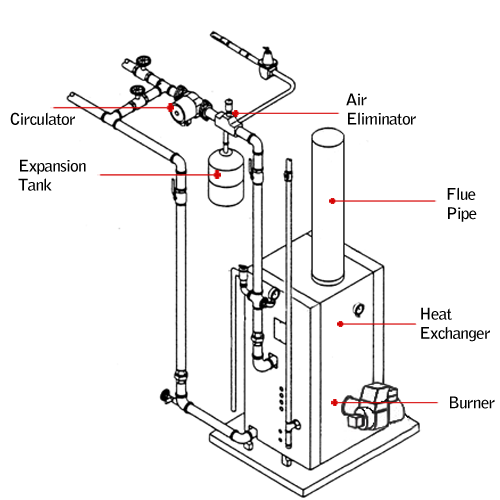
Burner: | The burner is the means through which the fuel is delivered to the system, ignited by a hot surface igniter, and burned in an efficient, controlled environment. |
Heat Exchanger: | Heat produced from the burning fuel in the burner is transferred to the metal walls of the heat exchanger. |
Circulator: | The circulator creates the flow for the system, drawing water over the heated walls of the heat exchanger and out into the system. |
Zone Valves: | Zone valves control the flow of hot water to different parts of the home.
|
Air Eliminator: | Water often has air bubbles in it which can cause components in the heat system to function poorly, the air eliminator siphons the air out of the water in the heat system. |
Expansion Tank: | The expansion tank is a tank with a bladder in it that allows the water to expand and contract as it is heated without putting undue stress on the boiler itself. |
Flue or Vent Pipe: | The flue or vent pipe serves to exhaust byproducts of the combustion process to the outside. |
Method of Heat Distribution: | Boiler systems are unique in that they allow a wide variety of distribution systems, such as baseboard heat, radiators, radiant tubing systems, and coils. |