Thermostat: | The thermostat acts a control, monitoring the temperature of the house, and brings the furnace on when the house needs to be heated. |
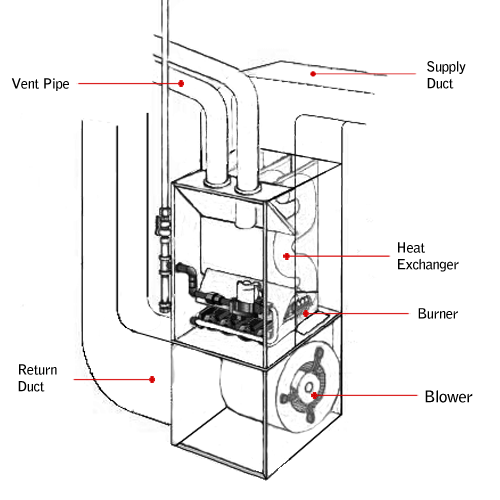
Burner: | The burner is the means through which the fuel is delivered to the system, ignited by a hot surface igniter, and burned in an efficient, controlled environment. |
Heat Exchanger: | Heat produced from the burning fuel in the burner is transferred to the metal walls of the heat exchanger. The heat exchanger also serves as a divide
between the source of combustion and the air distributed throughout the house, ensuring that harmful byproducts are not released into the household. |
Blower Motor: | The blower motor creates an air current that pulls air from the return ductwork, across the heat exchanger, and into the supply ductwork. |
Ductwork: | The ductwork transfers cooled air from the household to the furnace and the heated air from the furnace throughout the home. |
Flue or Vent Pipe: | The flue or vent pipe serves to exhaust byproducts of the combustion process to the outside. |