Thermostat: | The thermostat acts a control, monitoring the temperature of the house, and determining in which mode the system should be functioning. |
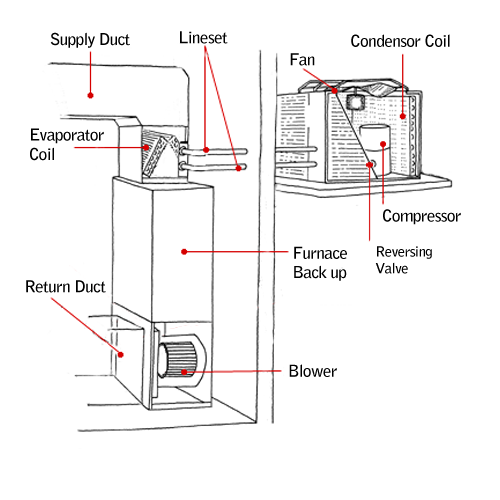
Reversing valve: | The reversing valve controls the direction of refrigerant flow. The flow determines whether the system is providing heating or cooling. |
Lineset: | The Lineset consists of two pipes connecting the indoor and outdoor units, one carrying refrigerant in a gaseous form, the other, in a liquid. |
Compressor: | The compressor resides in the outdoor unit and is responsible for compressing the refrigerant in the system from a gas into a liquid. |
Condenser: | The condenser is one of the two sets of coils containing refrigerant. When the unit is set to provide heat, the outside coils act as the condenser
while the indoor coil functions as the evaporator. In cooling mode, these two are reversed. In the condenser heat is extracted from the air as the refrigerant turns into a gas.
The gaseous refrigerant is sent via a lineset to the evaporator coils. |
Evaporator: | In the evaporator coils, the refrigerant releases the heat stored in it and begins to turn back into a liquid. |
Air handler: | The air handler is a blower system that blows air across the evaporator coils extracting the heat (or in the case of cooling, blowing the hot air over the
coil for the heat to be extracted)into the system’s ductwork, and into your home. |